Previously on … Network Namespaces - Part Two we provided internet access to the namespace, enabled a different DNS than our system and run a graphical application (xterm/firefox) from within.
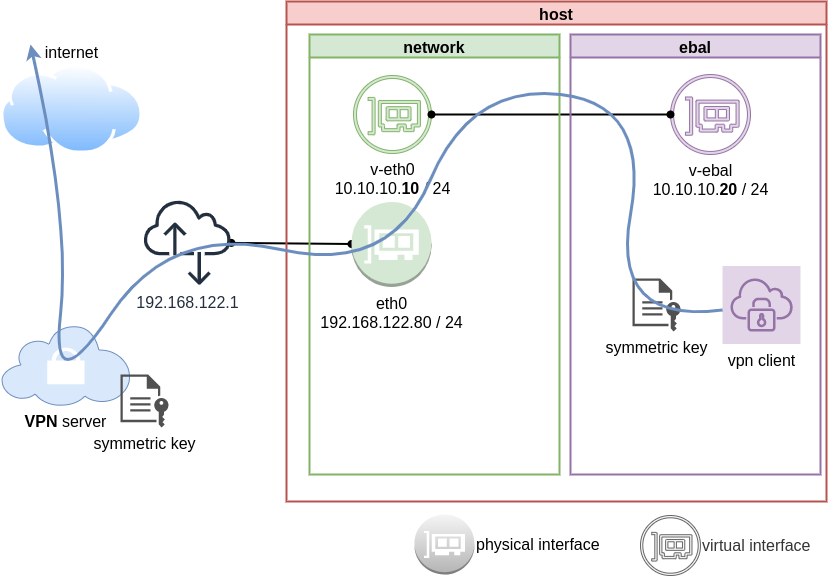
The scope of this article is to run vpn service from this namespace. We will run a vpn-client and try to enable firewall rules inside.
dsvpn
My VPN choice of preference is dsvpn and you can read in the below blog post, how to setup it.
dsvpn is a TCP, point-to-point VPN, using a symmetric key.
The instructions in this article will give you an understanding how to run a different vpn service.
Find your external IP
Before running the vpn client, let’s see what is our current external IP address
ip netns exec ebal curl ifconfig.co
62.103.103.103
The above IP is an example.
IP address and route of the namespace
ip netns exec ebal ip address show v-ebal
375: v-ebal@if376: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether c2:f3:a4:8a:41:47 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.10.10.20/24 scope global v-ebal
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::c0f3:a4ff:fe8a:4147/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
ip netns exec ebal ip route show
default via 10.10.10.10 dev v-ebal
10.10.10.0/24 dev v-ebal proto kernel scope link src 10.10.10.20
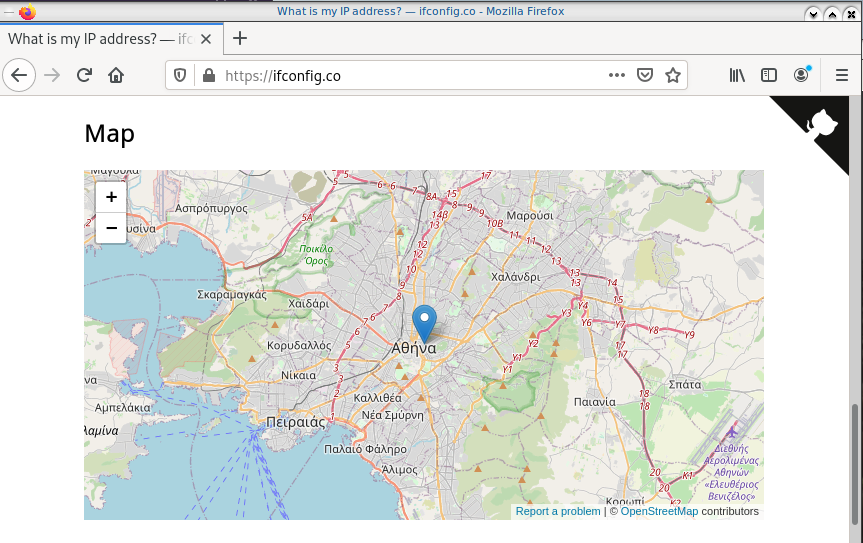
Firefox
Open firefox (see part-two) and visit ifconfig.co we noticed see that the location of our IP is based in Athens, Greece.
ip netns exec ebal bash -c "XAUTHORITY=/root/.Xauthority firefox"
Run VPN client
We have the symmetric key dsvpn.key and we know the VPN server’s IP.
ip netns exec ebal dsvpn client dsvpn.key 93.184.216.34 443
Interface: [tun0]
Trying to reconnect
Connecting to 93.184.216.34:443...
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbr
Connected
Host
We can not see this tunnel vpn interface from our host machine
# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 94:de:80:6a:de:0e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
376: v-eth0@if375: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 1a:f7:c2:fb:60:ea brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns ebal
netns
but it exists inside the namespace, we can see tun0 interface here
ip netns exec ebal ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
3: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 9000 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 500
link/none
375: v-ebal@if376: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether c2:f3:a4:8a:41:47 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
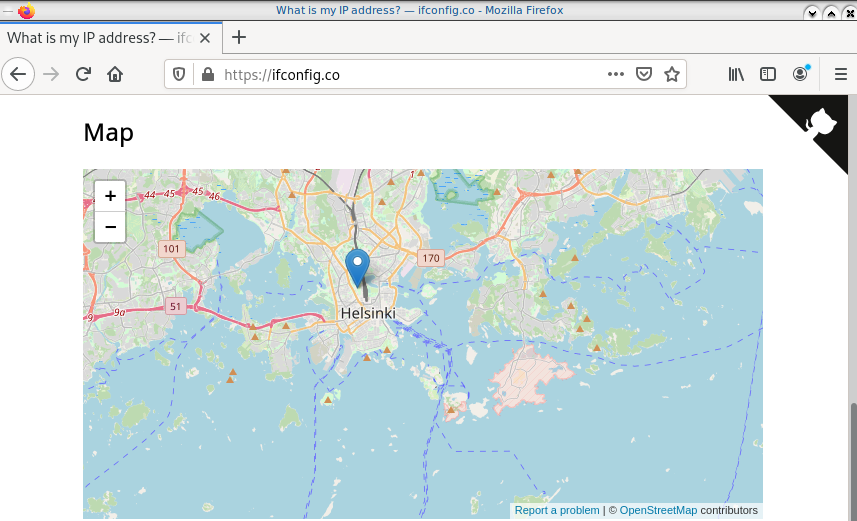
Find your external IP again
Checking your external internet IP from within the namespace
ip netns exec ebal curl ifconfig.co
93.184.216.34Firefox netns
running again firefox, we will noticed that our the location of our IP is based in Helsinki (vpn server’s location).
ip netns exec ebal bash -c "XAUTHORITY=/root/.Xauthority firefox"
systemd
We can wrap the dsvpn client under a systemcd service
[Unit]
Description=Dead Simple VPN - Client
[Service]
ExecStart=ip netns exec ebal /usr/local/bin/dsvpn client /root/dsvpn.key 93.184.216.34 443
Restart=always
RestartSec=20
[Install]
WantedBy=network.targetStart systemd service
systemctl start dsvpn.service
Verify
ip -n ebal a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
4: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 9000 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500
link/none
inet 192.168.192.1 peer 192.168.192.254/32 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 64:ff9b::c0a8:c001 peer 64:ff9b::c0a8:c0fe/96 scope global
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::ee69:bdd8:3554:d81/64 scope link stable-privacy
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
375: v-ebal@if376: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether c2:f3:a4:8a:41:47 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.10.10.20/24 scope global v-ebal
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::c0f3:a4ff:fe8a:4147/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
ip -n ebal route
default via 10.10.10.10 dev v-ebal
10.10.10.0/24 dev v-ebal proto kernel scope link src 10.10.10.20
192.168.192.254 dev tun0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.192.1
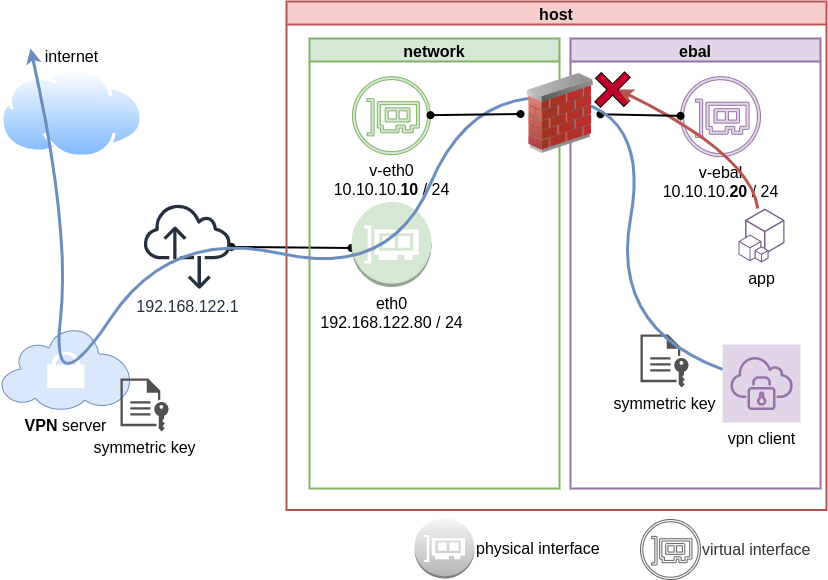
Firewall
We can also have different firewall policies for each namespace
outside
# iptables -nvL | wc -l
127
inside
ip netns exec ebal iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 9 packets, 2547 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 2 packets, 216 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
So for the VPN service running inside the namespace, we can REJECT every network traffic, except the traffic towards our VPN server and of course the veth interface (point-to-point) to our host machine.
iptable rules
Enter the namespace
inside
ip netns exec ebal bash
Before
verify that iptables rules are clear
iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 25 packets, 7373 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 376 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Enable firewall
./iptables.netns.ebal.sh
The content of this file
## iptable rules
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate INVALID -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT
## netns - incoming
iptables -A INPUT -i v-ebal -s 10.0.0.0/8 -j ACCEPT
## Reject incoming traffic
iptables -A INPUT -j REJECT
## DSVPN
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp -o v-ebal -d 93.184.216.34 --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
## net-ns outgoing
iptables -A OUTPUT -o v-ebal -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j ACCEPT
## Allow tun
iptables -A OUTPUT -o tun+ -j ACCEPT
## Reject outgoing traffic
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j REJECT --reject-with tcp-reset
iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
After
iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 DROP all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate INVALID
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 8 ctstate NEW
1 349 ACCEPT all -- v-ebal * 10.0.0.0/8 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 DROP all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate INVALID
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 8 ctstate NEW
0 0 ACCEPT all -- v-ebal * 10.0.0.0/8 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * v-ebal 0.0.0.0/0 95.216.215.96 tcp dpt:8443
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * v-ebal 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.0/8
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * tun+ 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with tcp-reset
0 0 REJECT udp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * v-ebal 0.0.0.0/0 95.216.215.96 tcp dpt:8443
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * v-ebal 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.0/8
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * tun+ 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with tcp-reset
0 0 REJECT udp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
PS: We reject tcp/udp traffic (last 2 linew), but allow icmp (ping).
End of part three.