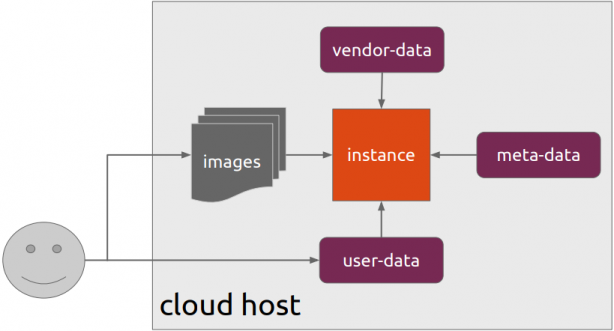
Cloud-init is the defacto multi-distribution package that handles early initialization of a cloud instance
This article is a mini-HowTo use cloud-init with centos7 in your own libvirt qemu/kvm lab, instead of using a public cloud provider.
How Cloud-init works
Josh Powers @ DebConf17
How really works?
Cloud-init has Boot Stages
- Generator
- Local
- Network
- Config
- Final
and supports modules to extend configuration and support.
Here is a brief list of modules (sorted by name):
- bootcmd
- final-message
- growpart
- keys-to-console
- locale
- migrator
- mounts
- package-update-upgrade-install
- phone-home
- power-state-change
- puppet
- resizefs
- rsyslog
- runcmd
- scripts-per-boot
- scripts-per-instance
- scripts-per-once
- scripts-user
- set_hostname
- set-passwords
- ssh
- ssh-authkey-fingerprints
- timezone
- update_etc_hosts
- update_hostname
- users-groups
- write-files
- yum-add-repo
Gist
Cloud-init example using a Generic Cloud CentOS-7 on a libvirtd qmu/kvm lab · GitHub
Generic Cloud CentOS 7
You can find a plethora of centos7 cloud images here:
Download the latest version
$ curl -LO http://cloud.centos.org/centos/7/images/CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2.xz
Uncompress file
$ xz -v --keep -d CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2.xz
Check cloud image
$ qemu-img info CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2
image: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 8.0G (8589934592 bytes)
disk size: 863M
cluster_size: 65536
Format specific information:
compat: 0.10
refcount bits: 16
The default image is 8G.
If you need to resize it, check below in this article.
Create metadata file
meta-data are data that comes from the cloud provider itself. In this example, I will use static network configuration.
cat > meta-data <<EOF
instance-id: testingcentos7
local-hostname: testingcentos7
network-interfaces: |
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.122.228
network 192.168.122.0
netmask 255.255.255.0
broadcast 192.168.122.255
gateway 192.168.122.1
# vim:syntax=yaml
EOF
Crete cloud-init (userdata) file
user-data are data that comes from you aka the user.
cat > user-data <<EOF
#cloud-config
# Set default user and their public ssh key
# eg. https://github.com/ebal.keys
users:
- name: ebal
ssh-authorized-keys:
- `curl -s -L https://github.com/ebal.keys`
sudo: ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
# Enable cloud-init modules
cloud_config_modules:
- resolv_conf
- runcmd
- timezone
- package-update-upgrade-install
# Set TimeZone
timezone: Europe/Athens
# Set DNS
manage_resolv_conf: true
resolv_conf:
nameservers: ['9.9.9.9']
# Install packages
packages:
- mlocate
- vim
- epel-release
# Update/Upgrade & Reboot if necessary
package_update: true
package_upgrade: true
package_reboot_if_required: true
# Remove cloud-init
runcmd:
- yum -y remove cloud-init
- updatedb
# Configure where output will go
output:
all: ">> /var/log/cloud-init.log"
# vim:syntax=yaml
EOF
Create the cloud-init ISO
When using libvirt with qemu/kvm the most common way to pass the meta-data/user-data to cloud-init, is through an iso (cdrom).
$ genisoimage -output cloud-init.iso -volid cidata -joliet -rock user-data meta-data
or
$ mkisofs -o cloud-init.iso -V cidata -J -r user-data meta-data
Provision new virtual machine
Finally run this as root:
# virt-install
--name centos7_test
--memory 2048
--vcpus 1
--metadata description="My centos7 cloud-init test"
--import
--disk CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2,format=qcow2,bus=virtio
--disk cloud-init.iso,device=cdrom
--network bridge=virbr0,model=virtio
--os-type=linux
--os-variant=centos7.0
--noautoconsole
The List of Os Variants
There is an interesting command to find out all the os variants that are being supported by libvirt in your lab:
eg. CentOS
$ osinfo-query os | grep CentOS
centos6.0 | CentOS 6.0 | 6.0 | http://centos.org/centos/6.0
centos6.1 | CentOS 6.1 | 6.1 | http://centos.org/centos/6.1
centos6.2 | CentOS 6.2 | 6.2 | http://centos.org/centos/6.2
centos6.3 | CentOS 6.3 | 6.3 | http://centos.org/centos/6.3
centos6.4 | CentOS 6.4 | 6.4 | http://centos.org/centos/6.4
centos6.5 | CentOS 6.5 | 6.5 | http://centos.org/centos/6.5
centos6.6 | CentOS 6.6 | 6.6 | http://centos.org/centos/6.6
centos6.7 | CentOS 6.7 | 6.7 | http://centos.org/centos/6.7
centos6.8 | CentOS 6.8 | 6.8 | http://centos.org/centos/6.8
centos6.9 | CentOS 6.9 | 6.9 | http://centos.org/centos/6.9
centos7.0 | CentOS 7.0 | 7.0 | http://centos.org/centos/7.0
DHCP
If you are not using a static network configuration scheme, then to identify the IP of your cloud instance, type:
$ virsh net-dhcp-leases default
Expiry Time MAC address Protocol IP address Hostname Client ID or DUID
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2018-11-17 15:40:31 52:54:00:57:79:3e ipv4 192.168.122.144/24 - -
Resize
The easiest way to grow/resize your virtual machine is via qemu-img command:
$ qemu-img resize CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2 20G
Image resized.$ qemu-img info CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2
image: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 20G (21474836480 bytes)
disk size: 870M
cluster_size: 65536
Format specific information:
compat: 0.10
refcount bits: 16You can add the below lines into your user-data file
growpart:
mode: auto
devices: ['/']
ignore_growroot_disabled: falseThe result:
[root@testingcentos7 ebal]# df -h /
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 20G 870M 20G 5% /
Default cloud-init.cfg
For reference, this is the default centos7 cloud-init configuration file.
# /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg users:
- default
disable_root: 1
ssh_pwauth: 0
mount_default_fields: [~, ~, 'auto', 'defaults,nofail', '0', '2']
resize_rootfs_tmp: /dev
ssh_deletekeys: 0
ssh_genkeytypes: ~
syslog_fix_perms: ~
cloud_init_modules:
- migrator
- bootcmd
- write-files
- growpart
- resizefs
- set_hostname
- update_hostname
- update_etc_hosts
- rsyslog
- users-groups
- ssh
cloud_config_modules:
- mounts
- locale
- set-passwords
- rh_subscription
- yum-add-repo
- package-update-upgrade-install
- timezone
- puppet
- chef
- salt-minion
- mcollective
- disable-ec2-metadata
- runcmd
cloud_final_modules:
- rightscale_userdata
- scripts-per-once
- scripts-per-boot
- scripts-per-instance
- scripts-user
- ssh-authkey-fingerprints
- keys-to-console
- phone-home
- final-message
- power-state-change
system_info:
default_user:
name: centos
lock_passwd: true
gecos: Cloud User
groups: [wheel, adm, systemd-journal]
sudo: ["ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL"]
shell: /bin/bash
distro: rhel
paths:
cloud_dir: /var/lib/cloud
templates_dir: /etc/cloud/templates
ssh_svcname: sshd
# vim:syntax=yaml